Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Leadership Competencies of Public Elementary School Heads and its Impact on Job Satisfaction of Teachers in the District of Victoria, Division of Laguna
Authors: Eloisa H. Tumbokon
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.54937
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This study aimed to determine the level of leadership competencies of public elementary school heads and its impact on job satisfaction of teachers in the District of Victoria, Division of Laguna. This study is limited to the three public elementary schools in the District of Victoria, Division of Laguna namely Victoria Elementary School, Masapang Elementary School, and Banca Elementary School. The researcher selects fifty (50) teachers per school as the respondents of the study. A total of one hundred fifty (150) teacher-respondents. The study used the Slovins Formula with 10% of margin of error in determining the sample respondents per school. The study used the descriptive survey research utilizing the researcher made instrument. The instrument consisted of the leadership competencies of school heads in terms of managerial leadership competencies, core behavioral competencies, and core skills, and the job satisfaction of teachers in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress, and goal support. The study found out that in general, the level of leadership competencies of public elementary school heads with respect to core behavioral competencies, managerial leadership competencies and core skills is Highly Competent. It may mean that the school heads demonstrated all the time the leadership competencies of a school leaders that can hone their knowledge and competence in leading the people and institution. Likewise, in general, the teachers are satisfied on the level of their job satisfaction in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress, and goal support. It may mean that the teachers are complacent for the resources and learning opportunities provided for them that can lead to better professional development. It was statistically found out that there is a significant relationship between the leadership competencies of school heads and job satisfaction of teachers in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress and goal support, since the obtained p-value of 0.00 does not exceed at 0.05 level of significance, thus the null hypothesis is rejected. It simply shows that teachers are satisfied with their job due to the attention and support of the school heads. Further, it was concluded that the school heads of the public elementary schools in the District of Victoria, Division of Laguna are worthy of emulation having demonstrated as Highly Competent in the performance of their duties. Also, the elementary teachers in the District of Victoria, Division of Laguna are satisfied with their job. Then, the teachers’ work satisfaction is directly affected by the school administrators’ core skills and inversely affected by the managerial leadership and core behavioral competencies of the school heads.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Education is the primary agent of transformation towards sustainable development. It increases people's capacities to transform their visions for society into reality. It is the key that unlocks the door to modernization. Furthermore, education is considered the greatest instrument in equipping every individual with the necessary knowledge, information, and skills to become a productive citizen. It is also regarded as a very important factor that leads to the success of an individual and the progress of a nation.
As provided for the 1987 Constitution of the Philippines, Section 2, Article IV to wit “The State shall establish, maintain, and support a complete, adequate, and integrated system of education relevant to the needs of the people in the society.” Such provision of law mandates the educational system to keep abreast with the needs of the time, much hope is ascribed to education in preparing the youth by inculcating and developing among them qualities that must be optimized to ensure that they will have ability to cope with the changes brought about by global demands. To realize this, educational institutions need to equip the learners with lifelong learning skills so that they may become self-developed persons to meet the challenges of the changing society.
According to Mejorada (2015), schools are responsible in delivering quality education among the students. She also stressed that more than good governance an effective and efficient curricular program normally serves as a great investment for a better development of every students. The school is where the students discover and develop their potentials and skills in different areas of specialization whether it is on academic or technical skills. School is the key for every student to achieve their dreams. It is where they are motivated to step forward to reach the top of their dreams.
In line with this framework of action, the Philippine EFA 2015 National Action Plan (UNESCO 2010) adopted in 2006 was formulated as the country's master plan for basic education. The cited provision reiterates the importance of education in nation building and gives chance to every Filipino to go to school and learn basic education.
In addition to being influenced by motivation, productivity is affected by worker’s ability and a number of situational and environmental factors. The objectives of the school will not be achieved if there is no harmony in the school between how the teachers perform and the leadership style. However, it would be erroneous to assert that all school principals in this country fail to acknowledge the significance of good human relations in dealing with their teachers, because it is evident that leadership approach would likely vary from one principal to the other and in part due to situation.
This statement could be viewed as signifying that effective leadership should take into account people, processes system. The need for effective interaction between the staff and the leader in a school system cannot be over-emphasized when one considers the fact that no school problem can be treated effectively without the involvement of all concerned. In public elementary schools, school heads are being appointed based on their qualifications and experiences. In every school where they are assigned, they usually meet problems on school development as well as for the work satisfaction of the teachers. Therefore, school administrators should make programs that are aligned to the needs of every teacher at school. Since, schools are being held accountable to the highest level of standards, especially in basic education, strong leadership is critical for its success. Thus, the positive outcomes of any educational institutions depend on the effectiveness of leadership employed that could lead to success and harmonious relationship.
These are the reasons why the researcher was motivated to investigate on the level of core skills competencies of public elementary school administrators in the Division of Rizal which are believed to be the contributory to the job satisfaction of teachers. The findings of the study could be the basis for recommendation on plan of action for both school heads and teachers to strengthen their competencies and job satisfaction. The present study is anchored from the core competency theory as cited by Twin (2021). This theory of strategy was introduced by C.K. Prahalad and Gary Hamel that prescribes actions taken by firms to achieve competitive advantage in the workplace. The concept of this theory states that persons must play to their strengths or those areas of functions in which they have competencies. In addition, the theory also defines as a harmonized combination of multiple resources and skills that distinguish a firm in the workplace and therefore are the foundation of organizations competitiveness.
Also, the study is anchored the concept and principles of Leadership and Development Theory by Beauchamp (2018). This theory begins with distinguishing leadership skills from leadership traits. Leadership skills are essentially techniques or practices that leaders apply in advancing a group toward common goals. Leadership skills are readily taught, both inside and out of the classroom. That this can be learned behavior is fortunate because developing leaders seldom show up with these skills already highly developed. Meanwhile, leadership traits are different. They are essentially behaviors or characteristics that an individual inherently possesses. Leadership traits can be well developed in individuals at a surprisingly early age. These traits include motivation, energy, perseverance, intelligence, self-confidence, fairness, ability to trust others, integrity, and forgiveness. Paramount to all these traits is the ability to communicate well. While some may consider good communication a skill rather than a trait, it is critically important to be able to consolidate one's ideas and formulate a vision of how to express those ideas to others. Clarity of focus is the trait from which this ability emanates. Although all these traits can also be formally taught, they often manifest independently of any formal or informal leadership training. Trait-laden individuals are often those identified to pursue leadership opportunities early in their careers. Persons characterized as “born leaders” tend to be those that “present” with advanced leadership traits.
The researcher found that the cited theories are related to the present study, since the study assessed the leadership competencies of public elementary school heads in terms of core behavioral competencies, core skills, and managerial leadership competencies. The researcher believes that with the theories on core competency and leadership development, it can be great of help to school heads in improving their competencies and can develop job satisfaction among teachers in their jurisdiction. The researcher added that when the school administrators boost the morale and engagement of every teacher at school, increases the organization’s ability to deal with gaps, and reduces problems or headaches encountered by the school community. In addition, school administrators should be able to generate and communicate a vision, converting that vision to tactics and initiatives, and identifying and delegating tasks to talented individuals who can assist in reaching this vision. They are the great leaders who attract, hire, and inspire great people in the school community.
Based on the theory presented, a conceptual framework was designed to give direction and emphasis to the study. The conceptual model used in the study is the Coombs’ System Approach which is shown in figure 1 signifies the three elements in designing the Input, Process and Output (IPO).
Frame 1 represents the input of the study which comprises the one hundred sixty (160) teacher-respondents from selected elementary schools in District of Victoria, Division of Laguna who assessed the level of leadership competencies of public elementary school heads in terms of core behavioral competencies, managerial leadership competencies, and core skills; and the level of job satisfaction in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress, and goal support.
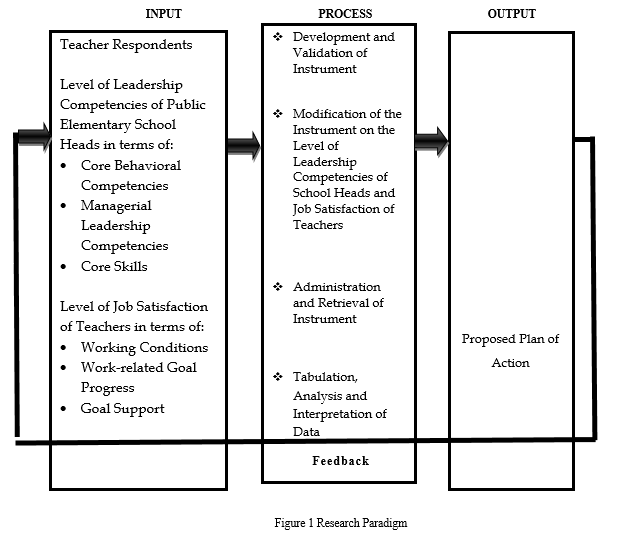
More so, Frame 2 refers to the process which includes the development and validation of the instrument; modification of the instrument on the level of leadership competencies of public elementary school heads in terms of core behavioral competencies, managerial leadership competencies, and core skills; and the level of job satisfaction in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress, and goal support; administration and retrieval of instrument; and tabulation, analysis, and interpretation of data to assess the relationship between the leadership competencies of public elementary school heads in terms of core behavioral competencies, managerial leadership competencies, and core skills; and the level of job satisfaction in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress, and goal support.
Frame 3 consists of the expected output of the study which is the proposed plan of action to further strengthen the competencies of school administrators and job satisfaction of teachers. Finally, the three frames are connected by a straight line to indicate the relationship between the input, process, and output. The arrow connecting the output and input provides feedback mechanism which indicates that there is a continuous process, which means that it is open for improvement and modification just in case there are still feedbacks and suggestions based on the result and findings of the research.
This study aimed to determine the leadership competencies of public elementary school heads in the District of Victoria, Division of Laguna and its impact on job satisfaction of teachers. The findings of the study served as the basis for recommendation in the improvement of leadership competencies of school heads. Specifically, this study sought to answer the following sub – problems: 1) What is the level of leadership competencies of public elementary school heads as assessed by the teacher-respondents in terms of managerial leadership competencies, core behavioral competencies, and core skills? 2) What is the level of job satisfaction of teachers as assessed by themselves in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress, and goal support? 3) Is there a significant relationship between level of leadership competencies of public elementary school heads and the level of job satisfaction of teachers? and 4) Based on the findings of the study, what recommendation may be proposed?
This study tested the hypothesis that there is no significant relationship between level of leadership competencies of public elementary school heads and the level of job satisfaction of teachers.
This study is designed to benefit the following: School Administrators may serve as an eye opener for them to realize their roles in improving the performance of the school as well as for the teachers. Teachers may be able to awaken their understanding on how to help their school heads to attain the improvement of the school especially in achieving quality of learning. Researchers may pursue hybrid studies in line with the competencies of school heads and its relation to job satisfaction of teachers.
This study is limited to the three public elementary schools in the District of Victoria, Division of Laguna namely Victoria Elementary School, Masapang Elementary School, and Banca Elementary School. The researcher selects fifty (50) teachers per school as the respondents of the study. A total of one hundred fifty (150) teacher-respondents. The study used the Slovins Formula with 10% of margin of error in determining the sample respondents per school. The study used the descriptive survey research utilizing the researcher made instrument. The instrument consisted of the core skills competencies of school heads in terms of leadership competencies, core behavioral competencies, and core skills; and the job satisfaction of teachers in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress, and goal support.
In order for the intended readers to fully understand the paper, the research has given both the conceptual and operational definition of the terms used in this paper. 1) Core Behavioral Competencies. This refers to any behavior attributes and personality traits of a school head might have such as self-management, professionalism and ethics, results focus, teamwork, service orientation, and innovation which can help determine how successful his/her organization. 2) Core Skills. These are essential skills that the school head needs to be fully prepared for life and work specification in the educational system such as oral and written communications, and computer/ ICT skills. 3) Leadership Competencies of School Administrators. This refers to the skills of the school heads that can contribute to the improvement of their personal competencies such as core behavioral competencies, managerial leadership competencies, and core skills which can greatly help in the development and progress of the schools. 4) Job Satisfaction. This refers to teachers’ contentedness with their job, whether they like the job or individual aspects such as nature of work or supervision. 5) Goal Support. This refers to the support received from superiors to overcome barriers specifically in relation to work goals and efficacy. 6) Managerial Leadership Competencies. This refers to the leadership skills and behaviors that contribute to superior performance. Also, this represents a combined set of knowledge, skills, and abilities that constitute effective leadership of the school heads within an organization. 7) Working Conditions. This refers to the working environment and aspects of a teacher’s terms and conditions of employment. 8) Work-Related Goal Progress. This refers to the teacher’s goal towards his/ her job such as improving time management, developing emotional intelligence and growth mindset.
II. METHODOLOGY
This section presents the research design, locale, sample and sampling technique, research instrument, data gathering procedure, statistical treatment of data, and ethical consideration.
This study utilized the descriptive correlational research designs since the study assessed the relationship between the leadership competencies of school heads and job satisfaction of teachers in the District of Victoria, Division of Laguna. According to Sousa (2020) descriptive correlational research design describes the variables and the relationship that occur naturally between and among them. The instrument used in the study was adapted from the OPCRF Manual. The researcher utilized this method since the study assessed the level of leadership competencies of school heads in terms of core behavioral competencies, managerial leadership competencies, and core skills; and the level of teachers’ job satisfaction in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress, and goal support.
The study conducted in the District of Victoria, Division of Laguna. The District of Victoria has ten (10) public elementary schools. The researcher selects three (3) public elementary schools based on the population of teachers. More so, the subjects of the study were the institutions in the District of Victoria which are highly recognized by the Division of Laguna in different pedagogical categories, both in academic and extra-curricular activities.
The respondents of the study were the three public elementary schools in the District of Victoria, Division of Laguna namely Victoria Elementary School, Masapang Elementary School, and Banca Elementary School. The researcher selects fifty (50) teachers per school as the respondents of the study. A total of one hundred fifty (150) teacher-respondents. The study used the Slovins Formula with 10% of margin of error in determining the sample respondents per school. The non-probability sampling especially the purposive sampling technique was used in selecting the respondents who assessed the level of leadership competencies of school heads and its impact to their job satisfaction.
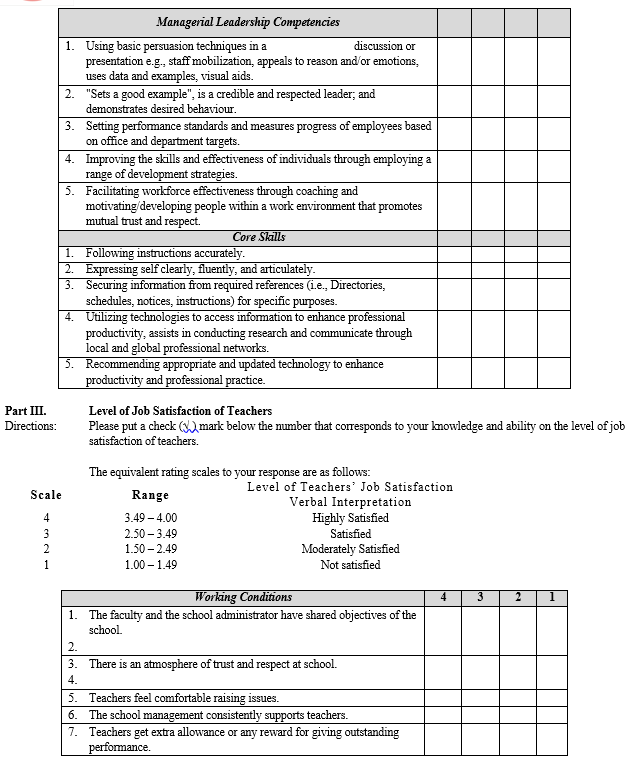
The study utilized a researcher-made instrument. The instrument was digital driven through the google form as the major tool of the study. The instrument was used to gather necessary data on the level of leadership competencies of school heads and its impact to the job satisfaction of teachers in public elementary schools in the District of Victoria, Division of Laguna. The instrument includes: Part 1 – This section determines the profile of the respondents. Part 2 – This section determines the level of leadership competencies of school heads as perceived by the teacher-respondents in terms of managerial leadership competencies, core behavioral competencies, and core skills. Part 3. This section pertains to the level of teachers’ job satisfaction as perceived by themselves in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress, and goal support.
The four (4) point scale below shows the range for the level of core skills competencies of school administrators and the level of teachers’ job satisfaction.
|
Scale |
Range |
Level of Leadership Competencies of School Heads |
Level of Teachers’ Job Satisfaction |
|
Verbal Interpretation |
Verbal Interpretation |
||
|
4 |
3.49 – 4.00 |
Highly Competent |
Highly Satisfied |
|
3 |
2.50 – 3.49 |
Competent |
Satisfied |
|
2 |
1.50 – 2.49 |
Moderately Competent |
Moderately Satisfied |
|
1 |
1.00 – 1.49 |
Not Competent |
Not satisfied |
Data collected in this study, follows the standard operating procedures. The instrument used in the study was submitted to the adviser in order to gather initial comments and suggestions for the improvement of the questionnaire checklist. After revision of the instrument had been made, the researcher’s made instrument was validated by the experts with the reasonable background in test construction and on the topic to comment on its content for the finalization of the items to be included in the instrument. Upon completion of the content validation form, permission from the office of the principals was sought by the researcher to administer the instrument to the respondents. Then, immediate retrieval of the instrument was done.
The following statistical tools used in this study. To determine the level of leadership competencies of school heads; mean was utilized. In order to determine the level of job satisfaction of teachers’ mean was applied. To find out if there is a significant relationship between the level of leadership competencies of school heads and teachers’ job satisfaction; Pearson ‘r’ correlation coefficient was utilized. In addition, the results gathered from the instrument were treated and interpreted using the appropriate statistical tools mentioned above.
The following were the ethical considerations observed by the researcher to ensure the integrity of the research process: 1) informed consent of the participants and respondents had been obtained before involving them in the study; 2) members of the sample group had not been subjected to coercion in any way; 3) privacy of the research respondents had been ensured, so that no personal data were collected from the respondents; 4) research respondents had been debriefed about the aims and objectives of the study before the primary data collection process ; 5) works that do not belong to the author of this paper had been acknowledged using APA referencing system in an appropriate format; 6) analysis of data was filtered through the researcher’s particular theoretical position and biases; 7) in case of harm inflicted by the researcher, the research was held responsible, and 8) top priority and confidentiality was maintained at all times during the conduct of the study.
III. RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
This section briefly presents the results, analysis, and interpretation of the data gathered based on the problems presented in the research.
A. Level Of Leadership Competencies Of Public Elementary School Heads As Assessed By The Teacher-Respondents
Table 1 presents the level of leadership competencies of public elementary school heads as assessed by the teacher-respondents in terms of core behavioral competencies.
Table 1
Level of Leadership Competencies of Public Elementary School Heads as Assessed by Teacher-Respondent in terms of Core Behavioral Competencies
|
Core Behavioral Competencies |
Mean |
Verbal Interpretation |
|
3.58 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.65 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.63 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.84 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.85 |
Highly Competent |
|
Overall |
3.71 |
Highly Competent |
***Legend HC – Highly Competent
It can be gleaned from the table that the overall mean of the level of leadership competencies of public elementary school heads as assessed by the teacher-respondents in terms of core behavioral competencies is 3.71 verbally interpreted as Highly Competent. It may mean that the school administrators demonstrated all the time with respect to their core behavioral competencies. Also, the school heads demonstrated strong core behavioral competencies that can help them, and their entire school community become well developed and organized.
It implies that effective leadership is not about making speeches or being liked, but a true leadership is defined by results of their competencies as a role model of every individual in the school community that may lead to the satisfaction of the teachers in the workplace.
This is consistent with the findings of Waweru, et al. (2020) stated that committed employees are likely to work harder and more efficiently and stay in their jobs longer than less committed employees. The study investigated the influence of principals’ (head of secondary schools) self-management on the organizational commitment (OC) of teachers as moderated by teachers’ self-efficacy. In the same manner, Suhardi (2020) said that teacher work productivity can affect the progress of the quality of learning in schools. This means that teacher work productivity can be increased through strengthening commitment to the profession and supervision of the principal.
Table 2 presents the level of leadership competencies of public elementary school heads as assessed by the teacher-respondents in terms of managerial leadership competencies.
Table 2
Level of Leadership Competencies of Public Elementary School Heads as Assessed by Teacher-Respondent in terms of Managerial Leadership Competencies
|
Managerial Leadership Competencies |
Mean |
Verbal Interpretation |
|
3.67 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.56 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.64 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.52 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.79 |
Highly Competent |
|
Overall |
3.64 |
Highly Competent |
***Legend HI – Highly Competent
It can be manifested from the table that the overall mean of the level of leadership competencies of public elementary school heads as assessed by the teacher-respondents in terms of managerial leadership competencies is 3.64 verbally interpreted as Highly Competent. It may mean that the school administrators demonstrated all the time with respect to their leadership competencies. More so, the school heads manifested great professional leadership competencies that hone their knowledge and competence in leading the people and institution.
It implies that school administrators had great leadership management skills towards its members in the school community. The researcher added that having a good leadership it can help the school heads in all aspects of their career in organizing and developing the best institution that they desire.
The findings are in parallel with the result of Hamid (2014) said that leader attributes contribute a stronger predictive effect than the motivation or keenness to lead in determining the selection of specific job characteristics. This finding supports the research hypothesis that undergraduates who have been exposed to leadership training and development have gained greater emotional and cognitive maturity that enable them to be more open to a broader range of job characteristic types.
Table 3 presents the level of leadership competencies of public elementary school heads as assessed by the teacher-respondents in terms of core skills.
Table 3
Level of Leadership Competencies of Public Elementary School Administrators as Assessed by Teacher-Respondent in terms of Core Skills
|
Core Skills |
Mean |
Verbal Interpretation |
|
3.58 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.79 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.68 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.59 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.67 |
Highly Competent |
|
Overall |
3.66 |
Highly Competent |
***Legend HI – Highly Competent
It can be depicted from the table that the overall mean of the level of leadership competencies of public elementary school heads as assessed by the teacher-respondents in terms of core skills is 3.66 verbally interpreted as Highly Competent. It may mean that the school heads demonstrated all the time with respect to their core skills. It means that the school heads demonstrated great professional core skills that hone their knowledge and competence in open communication in their jurisdiction.
This implies that school heads had great communication skills in dealing their people that lead them to productive and manageable working environment at all levels. Also, having good professional core skills it can help the school heads in maintaining healthy rapport with their colleagues. The findings suggest that school heads should attend seminars and trainings to strengthen their computer literacy skills. This goes with the findings of Karia (2019) that the emergence of employee leadership attributes, independently, has a significantly positive effect on work-related attitudes. Specifically, executive leadership has a significantly positive effect on organizational commitment, career satisfaction and job satisfaction, while innovative leadership has a significantly positive effect on organizational commitment and career satisfaction.
B. Level Of Job Satisfaction Of Teachers As Perceived By Themselves
Table 4 on the next page presents the level of job satisfaction of teachers as perceived by themselves in terms of working conditions.
Table 4
Level of Job Satisfaction of Teachers as Perceived by Themselves in terms of Working Conditions
|
Working Conditions |
Mean |
Verbal Interpretation |
|
3.26 |
Satisfied |
|
3.18 |
Satisfied |
|
2.65 |
Satisfied |
|
3.15 |
Satisfied |
|
3.28 |
Satisfied |
|
Overall |
3.10 |
Satisfied |
***Legend HI – Highly Competent
It can be gleaned from the table that the overall mean of the level of satisfaction of teachers in terms of working conditions is 3.10 verbally interpreted as Satisfied. It may mean that the teachers are contented in the working atmosphere and for the recognition or monetary allowance they received. It implies that the teachers are get satisfied with their job due to the support and supervision of the school heads. This goes with the findings of Baluyos (2019) said that Job satisfaction is a requirement for the work performance of the teacher. Findings revealed that the teachers were highly satisfied with their job, and their work performance was very satisfactory. The satisfaction of teachers on school heads’ supervision and job security inversely affects the teachers’ work performance. Schools must be provided with the faculty lounge so teachers can talk freely on their well-being.
Table 5 presents the level of job satisfaction of teachers as perceived by themselves in terms of work-related goal progress.
Table 5
Level of Job Satisfaction of Teachers as Perceived by Themselves in terms of Work-Related Goal Progress
|
Work-Related Goal Progress |
Mean |
Verbal Interpretation |
|
3.76 |
Highly Satisfied |
|
3.28 |
Satisfied |
|
3.16 |
Satisfied |
|
3.23 |
Satisfied |
|
3.34 |
Satisfied |
|
Overall |
3.35 |
Satisfied |
***Legend HI – Highly Competent
It can be manifested from the table that the overall mean of the level of satisfaction of teachers in terms of work-related goal progress is 3.35 verbally interpreted as Satisfied. It may mean that the teachers are complacent for the resources and learning opportunities provided for them that can lead to better professional development.
It implies that the teachers are well pleased with available resources and opportunities that are aligned with the goal of school’s improvement plan as well as to their professional development.
The result is in consonance with the study of Bashir (2017) that teaching is a highly noble profession and teachers are always a boon to the society. The ultimate process of education could be simplified as a meaningful interaction between the teacher and the taught. The teacher thus plays a direct and crucial role in molding a pupil towards education. Since a teacher is a role model for the students, job satisfaction and professional commitment of teachers become very vital in the fields of education. The result indicates that there exists a significant difference between male and female secondary school teachers in their job satisfaction and there exists no significant difference between male and female secondary school teachers in their professional commitment. Further result shows that there exists positive significant relationship between job satisfaction and professional commitment.
Table 6 on the next page presents the level of job satisfaction of teachers as perceived by themselves in terms of goal support.
Table 6
Level of Job Satisfaction of Teachers as Perceived by Themselves in terms of Goal Support
|
Goal Support |
Mean |
Verbal Interpretation |
|
3.87 |
Highly Satisfied |
|
3.01 |
Satisfied |
|
2.57 |
Satisfied |
|
2.89 |
Satisfied |
|
3.15 |
Satisfied |
|
Overall |
3.10 |
Satisfied |
***Legend HI – Highly Competent
It can be depicted from the table that the overall mean of the level of satisfaction of teachers in terms of goal support is 3.10 verbally interpreted as Satisfied.
It may mean that the teachers are satisfied with group discussions and collaborations with their co teachers that may lead to harmonious relationship and great success of their professional goals.
It implies that the teachers are happy in collaborating and interacting with their colleagues in making decisions to solve problems and accessing to different digital platforms that can provide quality of learning to their learners.
The result contradicts the findings of Hughes (2016) that many teachers in the Techiman Municipality perceived teaching as their ideal profession, but most teachers will prefer to change their profession as a result of dissatisfaction. Also, teachers felt their conditions of service were not good enough and most teachers in the Municipality felt dissatisfied with security in the profession.
C. Relationship Between The Level Of Leadership Competencies Of Public Elementary School Heads And Level Of Job Satisfaction Of Teachers
Table 7 presents the result of the significant relationship between the level of leadership competencies of public elementary school administrators and level of job satisfaction of teachers.
The table reveals that it was statistically found out that there is a significant relationship between the leadership competencies of school heads and job satisfaction of teachers in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress and goal support, since the obtained p-value of 0.00 does not exceed at 0.05 level of significance, thus the null hypothesis is rejected. It simply shows that teachers are satisfied with the working conditions, work-related goal progress and goal support due to the attention and support of the school heads.
Table 7
Relationship Between the Level of leadership Competencies of Public Elementary School Heads and Level of Job Satisfaction of Teachers
|
N |
Level of Teachers’ Job Satisfaction |
Pearson-r |
Sig. |
HO |
VI |
|
Core Behavioral Competencies |
Working Conditions |
.399 |
.506 |
FR |
NS |
|
Work-Related Goal Progress |
-.417 |
.485 |
FR |
NS |
|
|
Goal Support |
-.271 |
.659 |
FR |
NS |
|
|
Managerial Leadership Competencies |
Working Conditions |
.178 |
.774 |
FR |
NS |
|
Work-Related Goal Progress |
.332 |
.525 |
FR |
NS |
|
|
Goal Support |
.330 |
.587 |
FR |
NS |
|
|
Core Skills |
Working Conditions |
-.351 |
.033 |
R |
S |
|
Work-Related Goal Progress |
-.367 |
.030 |
R |
S |
|
|
Goal Support |
-.317 |
.063 |
FR |
S |
However, the core behavioral competencies and managerial leadership competencies of school administrators and the job satisfaction of teachers in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress and goal support are not significantly correlated, since the obtained p-value of 0.00 exceed at 0.05 level of significance, thus the null hypothesis is failed to reject. It may mean that the leadership styles of the school administrators are not quite visible to the teachers. It can be added that school heads must ensure that recognition for teachers with exemplary performance in the school should be done to boost their self-esteem and provide them with the feeling of security of their work.
The result implies that the school must invest and allocate an adequate amount for the professional development program of all teachers. They should not be confined only in the four walls of the classroom, but they must be allowed to keep abreast of all the updates in teaching.
They are duty bound to work with other people in the community aside from doing daily routines in education. Thus, training and workshops whether in local, national, or international that promote the better performance of teachers in teaching and in fostering activities that attract the people in the community to participate for the betterment of the school are necessary.
The findings are in consonant to the study of Baluyos (2019) stated that the teachers were highly satisfied with their job, and their work performance was very satisfactory.
The satisfaction of teachers on school heads’ supervision and job security inversely affects the teachers’ work performance. Schools must be provided with the faculty lounge so teachers can talk freely on their well-being.
IV. DISCUSSION
Following are the summary of findings obtained through the conduct of this study including the conclusions and recommendations formulated by the research.
A. Summary of Findings
- Level of Leadership Competencies of Public Elementary School Heads
In general, the level of leadership competencies of public elementary school heads with respect to core behavioral competencies, managerial leadership competencies and core skills is Highly Competent. It may mean that the school administrators demonstrated all the time the core skills competencies of a school leaders that can hone their knowledge and competence in leading the people and institution.
2. Level of Job Satisfaction of Teachers
In general, the teachers are satisfied on the level of their job satisfaction in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress, and goal support. It may mean that the teachers are complacent for the resources and learning opportunities provided for them that can lead to better professional development.
3. Relationship Between the Level of Leadership Competencies of Public Elementary School Heads and the Level of Job Satisfaction of Teachers
It was statistically found out that there is a significant relationship between the leadership competencies of school heads and job satisfaction of teachers in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress and goal support, since the obtained p-value of 0.00 does not exceed at 0.05 level of significance, thus the null hypothesis is rejected. It simply shows that teachers are satisfied with the working conditions, work-related goal progress and goal support due to the attention and support of the school heads.
However, the core behavioral competencies and managerial leadership competencies of school heads and the job satisfaction of teachers in terms of working conditions, work-related goal progress and goal support are not significantly correlated, since the obtained p-value of 0.00 exceed at 0.05 level of significance, thus the null hypothesis is failed to reject. It may mean that the leadership styles of the school heads are not quite visible to the teachers.
V. RECOMMENDATIONS
Based on the findings and conclusions, the following recommendations are hereby suggested:
- School heads may undergo seminars and training on the technology and different digital platforms that can enhance their core skills.
- School should always provide and seek strategic plan towards teacher’s professional growth and development that could improve the quality of learning of the learners in these trying times.
- School heads minimize their supervision on their teachers’ teaching performance but maximize their concern over the welfare of their teachers.
- A similar study may be conducted to validate the results of the study using other samples, variables, and in other contexts.
A. Proposed Plan Of Action To Further Strengthen The Leadership Competencies Of School Heads And Job satisfaction Of Teachers
The following set of intervention programs, projects and activities are carefully selected, planned, and organized in order to map a plan which hopes to strengthen the core skills competencies of school administrators and job satisfaction of teachers through this proposed action plan.
|
Objectives |
Activities/ Strategies |
Persons Involved |
Timetable |
|
To establish and convey visions, goals, and expectations of the school heads towards school improvement |
Establishing and stewarding the school’s mission and vision, setting goals and performance expectations, modeling aspirational practices, and promoting data for continual improvement of the school. |
Supervisors, School Heads, School Administrators, Head Teachers |
June 2021 |
|
To build professional capacity training to school heads in order for them to lead teacher learning and development |
Providing targeted and job-embedded professional development to meet school goals, building trusting relationships, protecting teachers’ time, and selecting new staff with right fit. |
Supervisors, School Heads, School Administrators, Head Teachers |
2nd week of June 2021 |
|
To create a supportive organization for learning |
Developing an organization where individuals are supported and valued by sharing and distributing leadership, understanding, and building on diversity, and strategically acquiring and allocating resources |
Supervisors, School Heads, School Administrators, Head Teachers |
3rd week of June 2021 |
|
To facilitate a high-quality learning experience for students |
Creating a high-quality instructional program by developing and monitoring curriculum, instruction, and assessment, and creating personalized learning environments that are safe and orderly |
Supervisors, School Heads, School Administrators, Head Teachers, Master Teachers, Teachers, Students |
4th week of June 2021 |
|
To give technical support to teachers through trainings and seminars in the different intervention that they could utilize in teaching the distance learning class such as using technology tools, applications, and platforms. |
Seminar workshop in using technology tools, applications, platforms |
School Head Teachers ICT Expert |
1st week of July 2021 |
|
To provide incentive program for deserving teachers who shows their excellent performance in the new normal |
|
School Head Teachers, parents, pupils, LGU DepEd officials, and other stakeholders |
1st week of July 2021 |


Conclusion
The following conclusions were formulated based on the findings presented: 1. The school heads of the public elementary schools in the District of Victoria, Division of Laguna are worthy of emulation having demonstrated as Highly Competent in the performance of their duties. 2. The elementary teachers in the District of Victoria, Division of Laguna are satisfied with their job. 3. The teachers’ work satisfaction is directly affected by the school heads’ core skills and inversely affected by the school heads’ managerial leadership and core behavioral competencies.
References
[1] Article XIV, Section 1 of the 1987 Philippine Constitution: Retrieved from: https://www.chanrobles.com/article14.htm#.YHGXWe [2] Baluyos, G.R. (2019). Teachers’ job satisfaction and work performance. Open Journal of Social Science, 7(8). [3] Bashir, L. (2017). Job satisfaction of teachers in relation to professional commitment. Lovely Professional University. [4] Beauchamp, N. Jr. J. (2018). Leadership and development Theory. Retrieved from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/ topics/ nursing-and-health- professions /leadership-development [5] Hughes, W.A. (2016). Assessing the impact of teacher job satisfaction among teachers. Journal of Education and Practice, 7(30). [6] Karia, N. (2019). Leadership attributes and their impact on work related attitude. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 65(5). [7] Mangaleswarasharma, R. (2017). Teacher motivation and job satisfaction: A study on teachers in three districts in Northern sri lanka. International Journal of Social Sciences, 3(1): 314-323. [8] Mejorada, N. (2015). Leadership attributes and their impact on work related Attitudes. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 65(5). [9] Rogers, P. (2017). Impact Evaluation, Better Evaluation. Retrieved from https://www.betterevaluation.org/en/themes/impact_ evaluation [10] Suhardi, E. (2020). Improvement of teacher work productivity through strengthening commitment to professionalism and supervision of school principals using correlational statistical analysis and sitorem methods. Journal of Humanities and Social Studies, 4(1). [11] Twin, A. (2021) Core Competencies. Investopedia. Retrieved from: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/core_com petencies.asp [12] Waweru, N.M. (2020). Influence of principals’ self-management on the organizational commitment of teachers in secondary school in county governments in Kenya. Independent Journal of Management and Production, 11(4).
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Eloisa H. Tumbokon. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET54937
Publish Date : 2023-07-23
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

